The capital market structure is a layer of the financial system. Here buyers and sellers interact for dealing in financial securities. In fact, the capital market is sub-part of a financial system. The other part of the financial system is the money market. In fact, the capital market structure provides structural foundations for long-term capital flow in India.
While the money market deals with short-term financing and its counterpart capital markets with the financing of long-term in nature. The primary aim of the capital market is to channelize those who have savings to those who need such savings. It generally involves a complex mechanism of institutions and systems.
What do you mean by the capital market?
The capital market is a sub-part of the financial market in India. It is a market where buyers and sellers participate in the trading of financial securities. Financial securities are generally of long-term investment nature. They may be shares of a company or bonds. Besides trading, corporates issue bonds and shares for the first time in the capital market to raise funds for their need. There is no physical place for such market. Instead, trading takes place electronically. A stock exchange facilitates such trading with various intermediaries like brokers etc.
What are the types of capital market?
Based on the instruments life and duration of its trading, the capital market is of two types. They are primary markets and secondary markets. The part of the capital market where firms and corporations issue securities for the first time are a primary capital market. In short, we call it the primary market. Likewise, the section of the capital market meant for trading in such instruments is the secondary capital market. In short, we call it the secondary market.
What is an example of a capital market structure in India?
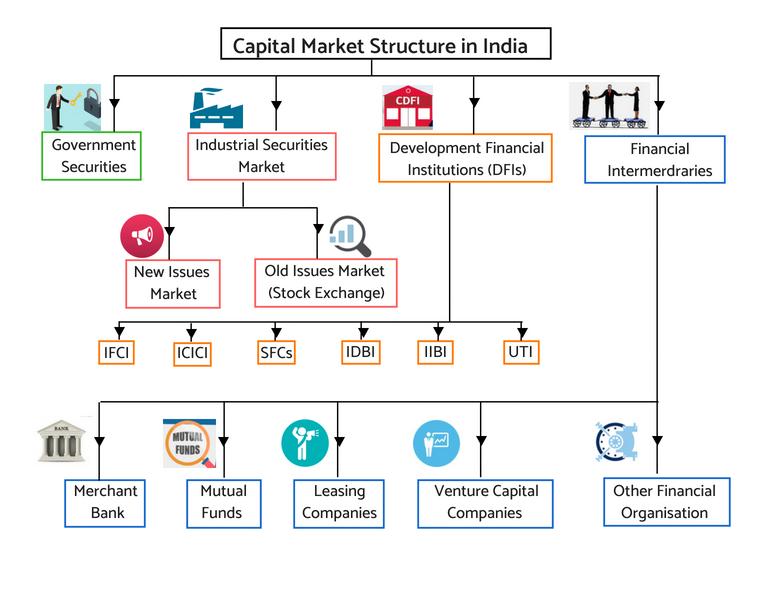
Capital market functions both in the formal and informal way. The formal capital market functions primarily through stock exchanges. While the informal markets run through “Dabba Trading” for secondary market trading in listed and unlisted stocks. At the same time the “Grey Market” for primary market dealing in stocks IPO. Thus, “Dabba Trading” and “Grey Market” are examples of the capital market in the informal segment.
On the other hand, stock exchanges in the organized or formal segment are the example of the formal capital market. In India, the National Stock Exchange (NSE), the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), the Multi-Commodity Exchange (MCX), the National Commodity and Derivative Exchange (NCDEX), etc. are an example of the capital markets informal segment.
What are the instruments in the Indian capital market structure?
The broad categories of tradable instruments of Indian capital market structure are –
- Equities
- Derivatives instruments
- Debt instruments
The equity market instruments are common stocks, Exchange traded funds, Indices, Initial public offerings, In Mutual funds, Offer for sale, Security lending, and borrowings.
Equity derivatives, currency derivatives, global indices derivatives and NSE bond futures comes under derivative instruments. Derivatives consist of future contracts, put options and call options.
At last the debt instruments includes corporate bonds and other debt instruments of central and state governments, Local bodies, Institutions, Public sector units, and Banks.
For a detailed list of instruments that NSE permits for trading, you can click here.
The capital market structure in India comprises of both primary markets and secondary markets. I explain briefly about both in the below paragraphs.
What is the primary capital market?
The primary capital market is a part of the capital market. This market is basically for issuing new securities in the market. Private companies, governments or public sector companies participate in primary markets. They come up with an initial public offering (IPO). These companies and institutions can also come up with the right issues and debt instruments through the primary market.
Through IPO, companies, and institutions raise money for the first time from the capital market. On the other hand, if a company wishes to raise money from their existing shareholders only, they do so through a right issue. Whereas in place of making shareholder, if institutions and companies wish to raise money, the issue of different bonds in the primary market. These bonds generally carry interest rate on them. Also, these instruments are for longer periods.
We also call the primary market as the new issue market (NIM).
What is the secondary capital market?
A secondary market is the part of the capital market where financial instruments already issued in primary markets are traded. Traded means bought and sold. Stock exchanges like NSE, BSE provides the facility for such trading. Financial instruments like stocks, bonds, derivatives, etc. are traded in the secondary market. Sometimes, we also call the secondary market as the aftermarket and follow-on public offering (FPO). In FPO, an existing company or institutions who already have raised money through IPO can raise money.
What is the difference between a primary and a secondary market?
The basic difference between the primary market and secondary market relies on when the money is being raised. If the issuer raises money for the first time then the primary capital market is the right place for such issues. However, if any existing entity, who already has raised money through primary market, do so through the secondary market.
We call the primary capital market in short as the primary market. Similarly, in short, we call the secondary capital market as the secondary market.
Both the primary market and secondary market is of immense help to a retail investor. With the understanding of both the capital market structure and knowledge of the distinction between primary and secondary capital market provide the edge to investors.
This helps in deciding when to invest through IPO, right issue or participate in the private placement and when to buy sell from the secondary market.
In general, when the market is in bull run it is always wise to invest in primary market instruments and when the market is in bear phase go for investments through the secondary market. If you avoid the primary market during the recession then chances of getting trapped in stocks with high pricing.
However, during a bull run, u need to be extra cautious in selecting stocks for investing. This is so because even low worth company flood the market with the offer.
What is the difference between money market and capital market?
The basic difference between the money market and the capital market is the life of instruments that are allowed to trade on such a platform. A money market in India is a place to park your money for a short duration. While on the other hand, very long-term investments are part of the capital market in India.
When it comes to the liquidity of the funds, the money market is the best place to invest in. Whereas when you need capital appreciation and not looking for any use of your money in the short run, you must go for the capital market.
Money market investments possess low risk as compared to capital market investments. Thus, risk-averse investors and those looking for hands ready money do good with money market instruments. Also, individuals seeking fixed income must use money market because of safety and timely return on their investments.
Various types of stocks and bonds are the instruments of the capital market. While deposits, bills of exchange, collateral loans, etc are money market-linked instruments.
Though there exists the difference between money market and capital market. Yet both the money market and capital market are similar in some aspects. The main similarity between the capital market and money market is that both helps maintain adequate levels of funding that is necessary for business functioning.
In Fact, both markets are complementary to each other. Investors enter capital market in high return expectation and willingly take high risk. While when they are ready to compromise with returns with the risk they prefer money market. As money market instruments fetch lower returns in comparison to capital market instruments.
What is the difference between fixed income and equity?
The characteristics that differentiate fixed income from equity instruments are –
- How trade takes place for such instruments
- A way through which they make the profit, and
- The level of risk associated.
When you plan for investments in equity, you mainly look for all kind of stocks and shares of a company are usually trade on any stock exchange platform. Or you consider mutual funds that invest mainly in stocks. But fixed-income investment instruments include corporate and government bonds and debt based mutual funds. Fixed deposits at banks & post office, savings bank accounts, and recurring deposits are also fixed income instruments.
Equity is high-risk instruments but at the same time fetches high return. On the other hand, fixed income securities possess comparatively low risk and at the same time fetches low returns. The returns from equity investments vary. Returns may be negative in with such instruments. However, returns from fixed income securities do not vary.
What is the main difference between a stock and a bond?
The discussion on the capital market structure is incomplete in the absence of discussion on the debt market in India. So let us discuss briefly on it. As we know the Stocks or share of a company represents ownership while bonds are debt instruments. Bonds, in general, are debts of long-term nature. When a company declares dividends, then every shareholder gets its share of dividends. But bondholders do not get such benefits. They only receive interest on their holdings. Basically, on the basis of issuers, there are two main categories of the bond market in India. One relates to corporate bonds in India while the other the government bond market.
Want to know the basics about the structure of the capital market in India? Click here to read a blog on “Structure of capital market in India – an introduction”
Capital market structure in India – market participants infographics

Stock Trading Now trade in ₹9 Per Order or ₹ 999 Per Month Plans.
Future & Options Access F&O contracts with advanced tools for hedging and speculation.
Currency Trading Trade in major currency pairs and manage forex exposure efficiently.
Commodity Trading Diversify Trading with MCX & NCDEX by Trading in Gold, Silver, Base Metals, Energy, and Agri Products.
Margin Trading Funding Boost your buying power with upto 5X, Buy now Pay Later
Algo Trading Back test, Paper Trade your logic & Automate your strategies with low-latency APIs.
Trading View Leverage Trading View charts and indicators integrated into your trading platform.
Advanced Options Trading Execute multi-leg option strategies with precision and insights.
Stock Lending & Borrowing Earn passive income by lending stocks securely through SLB.
Foreign Portfolio Investment Enable NRIs and FPIs to invest in Indian markets with ease and compliance.
IPO Invest in upcoming IPOs online with real-time tracking and instant allotment updates.
Direct Mutual Funds 0% Commissions by investing in more than +3500 Direct Mutual Fund Scheme.
Corporate FDRs Earn fixed returns with low-risk investments in high-rated corporate fixed deposits.
Stocks SIPs Build long-term wealth with systematic investment plans in top-performing stocks.
Bonds & NCDs Access secure, fixed-income investments through government and corporate bond offerings.
Depository Services Safely hold and manage your securities with seamless Demat and DP services with CDSL.
Journey Tracing our growth and milestones over time.
Mission & Vision Guided by purpose, driven by long-term vision.
Why RMoney Platform Smart, reliable platform for all investors' needs.
Management Experienced leadership driving strategic financial excellence.
Credentials Certified expertise with trusted industry recognition.
Press Release Latest company news, updates, and announcements.
Testimonials Real client stories sharing their success journeys.
7 Reasons to Invest Top benefits that make investing with us smart.
SEBI Registered Research Trusted insights backed by SEBI-compliant research.
Our Technology Advanced tools enabling efficient online trading.
Calculators Access a suite of smart tools to plan trades, margins, and returns effectively.
Margin Calculator Instantly check margin requirements for intraday and delivery trades.
MTF Calculator Calculate MTF funding cost upfront to ensure full transparency before placing a trade.
Brokerage Calculator Know your exact brokerage charges before placing any trade.
Market Place Explore curated investment products and trading tools in one convenient hub.
RMoney Gyan Enhance your market knowledge with expert blogs, videos, and tutorials.
Performance Tracker Track our research performance with full transparency using our performance tracker.
Feedback Share your suggestions or concerns to help us improve your experience.
Downloads Access important forms, software, and documents in one place.
Locate Us Find the nearest RMoney branch or service center quickly.
Escalation Matrix Resolve issues faster with our structured support escalation process.
Back Office Log in to view trade reports, ledger, and portfolio statements anytime.
Account Modification Update personal or bank details linked to your trading account.
Fund Transfer Transfer funds instantly online with quick limit updation to your trading account.
Bank Details View our registered bank account details for seamless transactions by NEFT, RTGS or IMPS.
How to Apply IPO Step-by-step guide to apply for IPOs using your trading account.
RMoney Quick Mobile App Trade on-the-go with our all-in-one mobile trading app.
RMoney Quick login Quickly access your trading account through the RMoney Quick web-based trading.
RMoney Rocket Web Version Experience powerful web-based trading with advanced tools for algo traders.
RMoney Rocket Mobile Version Trade anytime, anywhere with our feature-rich mobile trading platform.